并行程序设计导论
OpenMP
- private(var),每个线程创建未初始化私有变量,地址不同
- firstprivate(var),每个线程利用父进程变量值创建私有变量,地址不同,初始值相同
- lastprivate(var),第一个线程与父进程变量地址相同,其余线程地址不同,最后一个线程的var值将赋值给父进程
默认最后有barrier,使用nowait可取消barrier
MPI分布式内存编程
communicator指一组可以互相发送消息的进程集合
init/finalize
1
2
3
4
| int MPI_Init(
int* argc, /* in/out */
char** argv[] /* in/out */
);
|
该函数通常应该是第一个被调用的MPI函数用于并行环境初始化
其后面的代码到MPI_Finalize()函数之前的代码在每个进程中都会被执行一次。
– 除MPI_Initialized()外, 其余所有的MPI函数应该在其后被调用。
– MPI系统将通过argc,argv得到命令行参数(也就是说main函数必须带参数,否则会出错)。
定义由用户启动的所有进程组成的communicator,称为MPI_COMM_WORLD
1
| int MPI_Finalize(void);
|
– 退出MPI系统, 所有进程正常退出都必须调用。 表明并行代码的结束,结束除主进程外其它进程。
– 串行代码仍可在主进程(rank = 0)上运行, 但不能再有MPI函数(包括MPI_Init())。
comm
1
| int MPI_Comm_size(MPI_Comm comm ,int* size);
|
通信域的进程数
| IN | OUT |
|---|
| comm | size |
| communicator | number of processes in the group of comm,通常为MPI_COMM_WORLD |
1
| int MPI_Comm_rank (MPI_Comm comm ,int* pid);
|
| IN | OUT |
|---|
| comm | pid |
| communicator | rank of the calling process in group of comm |
send/recv
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| int MPI_Send(
void *buff,
int count,
MPI_Datatype datatype,
int dest,
int tag,
MPI_Comm comm
);
|
变量all in
– void *buff:你要发送的变量。
– int count:你发送的消息的个数(注意:不是长度,例如你要发送一个int整数,这里就填写1,如要是发送“hello”字符串,这里就填写6(C语言中字符串未有一个结束符,需要多一位))。
– MPI_Datatype datatype:你要发送的数据类型,这里需要用MPI定义的数据类型,可在网上找到,在此不再罗列。
– int dest:目的地进程号,你要发送给哪个进程,就填写目的进程的进程号。
– int tag:消息标签,接收方需要有相同的消息标签才能接收该消息。
– MPI_Comm comm:通讯域。表示你要向哪个组发送消息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| int MPI_Recv(
void *buff,
int count,
MPI_Datatype datatype,
int source,
int tag,
MPI_Comm comm,
MPI_Status *status
);
|
out: buff, status
– void *buff:你接收到的消息要保存到哪个变量里。
– int count:你接收消息的消息的个数(注意:不是长度,例如你要发送一个int整数,这里就填写1,如要是发送“hello”字符串,这里就填写6(C语言中字符串未有一个结束符,需要多一位))。它是接收数据长度的上界. 具体接收到的数据长度可通过调用MPI_Get_count 函数得到。
– MPI_Datatype datatype:你要接收的数据类型,这里需要用MPI定义的数据类型,可在网上找到,在此不再罗列。
– int dest:接收端进程号,你要需要哪个进程接收消息就填写接收进程的进程号。
– int tag:消息标签,需要与发送方的tag值相同的消息标签才能接收该消息。
– MPI_Comm comm:通讯域。
– MPI_Status *status:消息状态。接收函数返回时,将在这个参数指示的变量中存放实际接收消息的状态信息,包括消息的源进程标识,消息标签,包含的数据项个数等。
MPI_Status:至少有MPI_SOURCE, MPI_TAG, MPI_ERROR,发送者/标签/error
1
2
3
4
5
| int MPI_Get_count(
MPI_Status* status_o /* in */,
MPI_Datatype type /* in */,
int* count_p /* out */
);
|
MPI_type
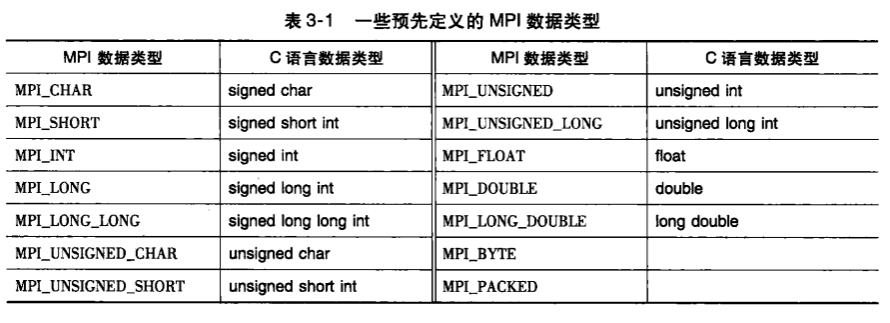
消息匹配
若q号进程调用了MPI_Send函数,r号进程调用了MPI_Recv函数,则前者消息可以被后者接受若:
recv_comm = send_commrecv_tag = send_tagdest = r,src = q- 前三对参数必须指定兼容的缓冲区
recv_type = send_type,同时recv_buf_size >= send_buf_size
避免接受进程排序接受造成发送进程的等待,MPI特殊常量MPI_ANY_SIZE作为source,传递给MPI_Recv
同理,对标签,MPI_ANY_TAG
发送方必须指定进程号和非负整数标签,通信子双方都需指定
IO
所有进程可输出,只有0号进程可访问标准输入stdin
通信方式
集合通信
- 在通信子中所有进程都必须调用相同的集合通信函数
- 每个进程传递给MPI集合通信函数的参数必须是相容的,
dest_process值相同 - 参数
output_data_p只用在dest_process上
点对点通信通过标签和通信子匹配,集合通信不使用标签,只通过通信子和调用的顺序来匹配
不能使用同一个缓冲区作为MPI输入输出
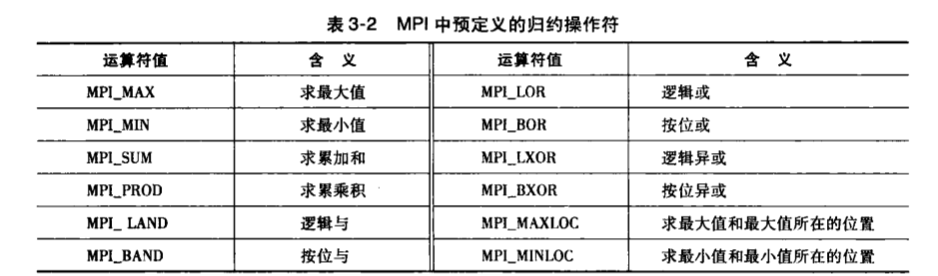
MPI_Reduce
全局求和/最大值/最小值/乘积
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| int MPI_Reduce(
void * input_data_p /* in */,
void * output_data_p /* out */,
int count /* in */,
MPI_Datatype datatype /* in */,
MPI_Op operator /* in */,
int dest_process /* in */,
MPI_Comm comm /* in */
);
|
operator:
MPI_Allreduce
所有进程想得到全局总和
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| int MPI_Allreduce(
void * input_data_p /* in */,
void * output_data_p /* out */,
int count /* in */,
MPI_Datatype datatype /* in */,
MPI_Op operator /* in */,
int dest_process /* in */,
MPI_Comm comm /* in */
);
|
广播
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| int MPI_Bcast(
void * data_p /* in/out */,
int count /* in */,
MPI_Datatype datatype /* in */,
MPI_Op operator /* in */,
int source_proc /* in */,
MPI_Comm comm /* in */
);
|
所有进程都执行,但source_proc进程发送,其他进程收取,
相当于同步各个进程中data_p内存地址的值,异步的
数据分发
如向量求和,3种划分方式:
块划分(连续),循环划分,块-循环划分
散射
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| int MPI_Scatter(
void * send_buf_p /* in */,
int send_count /* in */,
MPI_Datatype send_type /* in */,
void * recv_buf_p /* out */,
int recv_count /* in */,
MPI_Datatype recv_type /* in */,
int src_proc /* in */,
MPI_Comm comm /* in */
);
|
内部读取进程号,进行数据分发操作
聚集
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| int MPI_Gather(
void * send_buf_p /* in */,
int send_count /* in */,
MPI_Datatype send_type /* in */,
void * recv_buf_p /* out */,
int recv_count /* in */,
MPI_Datatype recv_type /* in */,
int dest_proc /* in */,
MPI_Comm comm /* in */
);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| int MPI_Allgather(
void * send_buf_p /* in */,
int send_count /* in */,
MPI_Datatype send_type /* in */,
void * recv_buf_p /* out */,
int recv_count /* in */,
MPI_Datatype recv_type /* in */,
MPI_Comm comm /* in */
);
|
allgather把分块合并,例如矩阵和向量相乘
评估
计时
1
| double MPI_Wtime(void);
|
派生数据类型
分布式内存系统中,通信比本地计算开销大很多,因此用多条消息发送一定数量的数据比只用一条消息发送等量的数据耗时
减少发送的消息数量,有助于提升程序性能
整合需要多条消息的数据
MPI_Pack/Unpack
派生数据类型:视作由多种MPI基本数据类型组合而成,包括数据类型,以及他们的偏移
于是发送数据可以将其整合
创建由不同基本数据类型的元素组成的派生数据类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| int MPI_Type_create_struct(
int count /* in */,
int array_of_blocklengths[] /* in */,
MPI_Aint array_of_displacements[] /* in */,
MPI_Datatype array_of_types[] /* in */,
MPI_Datatype* new_type_p /* out */
);
|
数组参数有count个元素
displacement单位字节
需要先初始化指定new_type_p:
1
| int MPI_Type_commit(MPI_Datatype* new_mpi_t_p /* in/out */);
|
填充array_of_displacements的值:
1
2
3
4
| int MPI_Get_address(
void* localtion_p /* in */,
MPI_Aint* address_p /* out */
);
|
返回location_p指向的内存单元的地址,将其存储到address_p指向的内存单元,将内存单元的值减去首个,即可得偏移量,将其存储到array_of_displacements每一位即可
使用新数据类型,每个进程上调用MPI_Bcast
释放:
1
| int MPI_Type_free(MPI_Datatype* old_mpi_t_p /* in/out */);
|
Pthread
pthread_t对象是不透明对象,数据是系统绑定的,用户级无法访问,但确实是现成的唯一标识
创建/停止
1
2
3
4
5
6
| int pthread_create(
pthread_t* thread_p /* out */,
const pthread_attr_t* attr_p /* in */,
void* (*start_routine)(void*) /* in */,
void* arg_p /* in */
);
|
pthread_t在调用前分配空间
1
2
3
4
| int pthread_join(
pthread_t thread /* in */,
void** ret_val_pm /* out */
);
|
等待pthread_t对象关联的线程结束
互斥量
保证一个线程独享临界区
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| int pthread_mutex_init(
pthread_mutex_t* mutex_p /* out */,
const pthread_mutexattr_t* attr_p /* in *,
);
int pthread_mutex_destroy(
pthread_mutex_t* mutex_p /* in/out */
);
int pthread_mutex_lock(
pthread_mutex_t* mutex_p /* in/out */
);
int pthread_mutex_unlock(
pthread_mutex_t* mutex_p /* in/out */
);
|
$$\frac{T_{串行}}{T_{并行}} \sim thread_count$$
若thread_count小于或等于核的个数,将其称作加速比,当加速比等于线程数则理想,线性加速比
信号量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| int sem_init(
sem_t* semaphore_p /* out */,
int shared /* in */,
unsigned initial_val /* in */
);
int sem_destroy(sem_t* semaphore_p /* in/out */);
int sem_post(sem_t* semaphore_p /* in/out */);
int sem_wait(sem_t* semaphore_p /* in/out */);
|
信号量,特殊类型unsigned int无符号整型变量
二元信号量初始化为1,0-上锁,1-未上锁;
wait,若信号量为0,则阻塞,否则减一进入临界区
post,信号量加一
macosx不支持普通方式,若要使用普通方式:
alternatives:
- Initialize the semaphore:
1
2
3
| #include <dispatch/dispatch.h>
dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore;
semaphore = dispatch_semaphore_create(1); // init with value of 1
|
1
2
3
| dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER);
...
dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore);
|
1
| dispatch_release(semaphore);
|
macosx专属:
sem_open替换sem_init,sem_close替换sem_destroy/sem_unlink
1
2
3
4
| #include <semaphore.h>
sem_t *
sem_open(const char *name, int oflag, ...);
|
会创建空间给sem_t,因此只需要事先声明指针。
The value of oflag:
O_CREAT create the semaphore if it does not existO_EXCL error if create and semaphore exists
若为O_CREAT,另外两个参数:mode, value
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| // <sys/stat.h>
#define S_IRWXU 0000700 /* RWX mask for owner */
#define S_IRUSR 0000400 /* R for owner */
#define S_IWUSR 0000200 /* W for owner */
#define S_IXUSR 0000100 /* X for owner */
#define S_IRWXG 0000070 /* RWX mask for group */
#define S_IRGRP 0000040 /* R for group */
#define S_IWGRP 0000020 /* W for group */
#define S_IXGRP 0000010 /* X for group */
#define S_IRWXO 0000007 /* RWX mask for other */
#define S_IROTH 0000004 /* R for other */
#define S_IWOTH 0000002 /* W for other */
#define S_IXOTH 0000001 /* X for other */
#define S_ISUID 0004000 /* set user id on execution */
#define S_ISGID 0002000 /* set group id on execution */
#define S_ISVTX 0001000 /* save swapped text even after use */
|
路障/条件变量
大部分pthread库不提供实现,手写:
忙等待/互斥量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| int counter;
int thread_count;
pthread_mutex_t barrier_mutex;
void* Thread_work(/*...*/){
/* Barrier */
pthread_mutex_lock(&barrier_mutex);
counter++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&barrier_mutex);
while(counter < thread_count) ;
// ...
}
|
信号量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| int counter;
int thread_count;
sem_t count_sem; // 保护计数器,初始化为1
sem_t barrier_sem; // 阻塞到达路障的线程
void* Thread_work(/*...*/){
/* Barrier */
sem_wait(&count_sem);
if(counter == thread_count - 1){
counter = 0;
sem_post(&barrier_sem);
for(j = 0; j < thread_count - 1; j++){
sem_post(&barrier_sem);
}
}
else{
counter++;
sem_post(&counter_sem);
sem_wait(&barrier_sem);
}
// ...
}
|
条件变量
允许线程在某个特定条件或事件发生前都处于挂起状态,事件发生时另一个线程唤醒此线程
一般用法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| lock mutex;
if condition has occured{
signal threads;
}
else{
unlock mutex and block;
}
unlock mutex;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| // 解锁一个被阻塞线程
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond_var_p /* in /out */);
// 广播 解锁所有线程
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond_var_p /* in /out */);
// 通过互斥量阻塞线程
int pthread_cond_wait(
pthread_cond_t * cond_var_p /* in /out */,
pthread_mutex_t * mutex_p /* in /out */
);
// 相当于执行以下代码:
// 先解锁,醒了之后再锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_p);
wait_on_signal(&cond_var_p);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_p);
|
实现路障:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| int counter;
int thread_count;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond_var;
void* Thread_work(/*...*/){
/* Barrier */
pthread_mutex_lock(&barrier_mutex);
counter++;
if(counter == thread_count){
counter = 0;
pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond_var);
}
else{
while(pthread_cond_wait(&cond_var, &mutex) != 0);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
// ...
}
|
读写锁
Member函数:使用指针遍历链表,找到目标Insert函数Delete函数
多线程链表,不允许正在执行Member函数的线程还可以同时访问链表的任意节点:
- 任意时刻只允许一个线程分访问整个链表
- 任意时刻只允许一个线程访问任意给定节点
与互斥量相似,但加入两个为读操作枷锁和为写操作枷锁的函数。
多个线程能够通过调用读函数获得锁
但只有一个线程能够通过写函数获得锁
若任何线程拥有读锁,则请求写锁的线程将阻塞在写锁函数,反之亦然
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| int pthread_rwlock_init(
pthread_rwlock_t* rwlock_p /* out */,
const pthread_rwlockattr_t* attr_p /* in */
);
int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t* rwlock_p /* in/out */);
int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t* rwlock_p /* in/out */);
int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t* rwlock_p /* in/out */);
int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t* rwlock_p /* in/out */);
|
实现
使用两个条件变量,对应读者、写者,以及一个互斥量
还包括一些成员,表示:
- 多少读者拥有锁
- 多少读者等待锁
- 是否有一个写者拥有锁
- 多少写者等待锁
OpenMP
允许程序员简单声明一块代码需要并行,具体线程执行方式由编译器和运行时系统来决定
编译:使用gcc-11 -Wall -fopenmp -o xxx xxx.c
开头,后面的第一条指令是一条parallel指令,
指定线程数:
1
| # paragma omp parallel num_threads(thread_count)
|
获得自己编号、总共的线程数:
1
2
| int omp_get_thread_num(void);
int omp_get_num_threads(void);
|
格式:
1
2
3
4
| #paragma omp construct [clause [clause]...]
{
// ...
}
|
constructs(可组合):
- parallel regions
- worksharing
#paragma omp for#paragma omp sections
- data environment
#paragma omp parallel shared/private (...)
- synchronization
- critical region
- cycle construction
#paragma omp for schedule(kind[,chunk_size])
- runtime functions/envirenment variables
int my_thread_id = omp_get_num_threads();omp_set_num_threads(8);
指定变量共享/私有:
1
| #pragma omp parallel private(xx);
|

