C#程序运行在.NET上,.NET由通用语言运行时(CLR)的虚拟执行系统和一组类库组成,CLR由微软国际标准通用语言基础结构(CLI)实现。C#源代码被编译为符合CLI规范的终极语言(IL),其代码与资源存储在.dll中。执行C#程序后,组件加载到CLR中,CLR执行JIT及时编译,将IL代码转化为本机指令,垃圾回收、异常处理、资源管理等服务由CLR提供。C#编译器生成的IL代码符合通用类型规范(CTS),不同高级语言编写的模块能够互相引用。
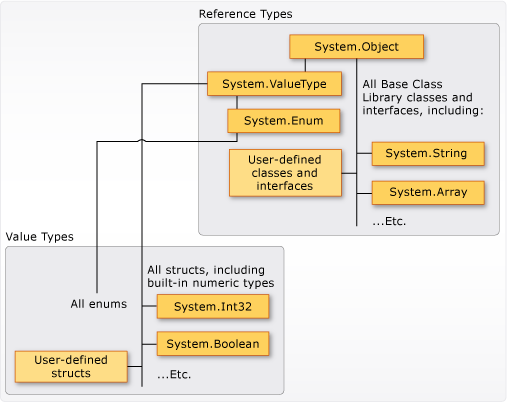
通用类型系统(CTS)
数据类型
- signed:
sbyte - unsigned:
byte, ushort, uint, ulong - high resolution decimal float point:
decimal - tuple:
() - empty:
null - ultimate class:
object - unicode string:
string - delegate types:
delegate int D(...)
在 C# 中,bool不能转换为 int,通常类型的值不允许为null,声明加入?即可允许
C++ auto => C# var
类型中可存储的信息:
记录类型可以是引用类型 (record class) 或值类型 (record struct)
值类型
值类型,比如结构,分配结构的变量保留结构的实际数据,将结构分配给新变量时,复制结构,更改不会互相改变
分为struct和enum,C#内置的数值类型是结构,具有可访问的字段和方法
值类型封闭,不能从任何值类型派生类型,结构只能从System.ValueType继承,但是结构可以实现多个接口,可以将结构强制类型转换为接口类型,导致装箱操作,将结构包装在托管堆上的引用类型对象内
struct
struct隐式源自System.ValueType
enum
枚举定义的是一组已命名的整型常量,所有枚举从 System.Enum(继承自 System.ValueType)继承
引用类型
引用类型,比如类创建对象后,分配对象的变量仅保留对内存的引用,对象引用分配给新变量后,仍然引用原始对象,更改对多个引用相同数据的变量生效
包含class、record、delegate、数组或 interface 的类型是 reference type
class
成员类型:
- 常量:与类相关联的常量值
- 字段:与类关联的变量
- 方法:类可执行的操作
- 属性:与读取和写入类的已命名属性相关联的操作
- 索引器:与将类实例编入索引(像处理数组一样)相关联的操作
- 事件:类可以生成的通知
- 运算符:类支持的转换和表达式运算符
- 构造函数:初始化类实例或类本身所需的操作
- 终结器:永久放弃类的实例之前完成的操作
- 类型:类声明的嵌套类型
访问控制:
public:访问不受限制。private:访问仅限于此类。protected:访问仅限于此类或派生自此类的类。internal:仅可访问当前程序集(.exe 或 .dll)。protected internal:仅可访问此类、从此类中派生的类,或者同一程序集中的类。private protected:仅可访问此类或同一程序集中从此类中派生的类。
属性可设置get/set方法的访问控制:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public class Person
{
public string? FirstName { get; private set; }
// Omitted for brevity.
}
|
sealed停止虚拟继承,针对方法
C++模板,在C#中为类型参数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public class Pair<TFirst, TSecond>
{
public TFirst First { get; }
public TSecond Second { get; }
public Pair(TFirst first, TSecond second) =>
(First, Second) = (first, second);
}
|
类包含的成员类型
- 常数: 与类关联的常数值
- 领域: 与类关联的变量
- 方法: 该类可以执行的操作
- 属性: 与阅读和写作类命名属性相关的操作
- 索引器: 与类实例索引相关的操作,例如数组
- 活动: 该类可以生成的通知
- 操作员: 类支持的转换和表达运算符
- 构造函数: 初始化类或类本身的实例所需的操作
- 最终确定者: 在永久丢弃该类实例之前执行的操作
- 类型: 该类声明的嵌套类型
每个.NET类型都有一个默认值,数字类型值为0,引用类型值为null,字段可使用初始化表达式设置初始值:
1
2
3
4
5
| public class Container
{
// Initialize capacity field to a default value of 10:
private int _capacity = 10;
}
|
C# 12开始,可以将构造函数定义为类声明的一部分:
1
2
3
4
| public class Container(int capacity)
{
private int _capacity = capacity;
}
|
还可以对某个属性使用 required 修饰符,并允许调用方使用对象初始值设定项来设置该属性的初始值:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class Person
{
public required string LastName { get; set; }
public required string FirstName { get; set; }
}
var p1 = new Person(); // Error! Required properties not set
var p2 = new Person() { FirstName = "Grace", LastName = "Hopper" };
|
方法主体为单个表达式时,紧凑表达式格式定义该方法,即=>记号
函数正常为值传参,指定默认值后可选;使用ref关键词定义的为参考参数,即引用传参;输出参数,out关键词指定,同样引用传参,out例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| static void Divide(int x, int y, out int quotient, out int remainder)
{
quotient = x / y;
remainder = x % y;
}
public static void OutUsage()
{
Divide(10, 3, out int quo, out int rem);
Console.WriteLine($"{quo} {rem}"); // "3 1"
}
|
params object[] args可变参数
静态方法(static修饰)通过类访问,实例方法通过实例访问,都使用.索引
虚拟virtual方法在基类中需要有实现,abstract方法在基类中没有实现,每个派生类都需要实现,仅在abstract class中存在,覆盖override方法在派生类中覆盖虚拟
其他职能类方法:constructors, properties, indexers, events, operators, and finalizers
properties是field的延伸,属性不表示实际存储的数据,而是自定的get/set方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
| public class MyList<T>
{
// fields
const int DefaultCapacity = 4;
T[] _items;
int _count;
// constructor
public MyList(int capacity = DefaultCapacity)
{
_items = new T[capacity];
}
// properties
public int Count => _count;
public int Capacity
{
get => _items.Length;
set
{
if (value < _count) value = _count;
if (value != _items.Length)
{
T[] newItems = new T[value];
Array.Copy(_items, 0, newItems, 0, _count);
_items = newItems;
}
}
}
// indexer
public T this[int index]
{
get => _items[index];
set
{
if (!object.Equals(_items[index], value)) {
_items[index] = value;
OnChanged();
}
}
}
public void Add(T item)
{
if (_count == Capacity) Capacity = _count * 2;
_items[_count] = item;
_count++;
OnChanged();
}
protected virtual void OnChanged() =>
Changed?.Invoke(this, EventArgs.Empty);
public override bool Equals(object other) =>
Equals(this, other as MyList<T>);
static bool Equals(MyList<T> a, MyList<T> b)
{
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(a, null)) return Object.ReferenceEquals(b, null);
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(b, null) || a._count != b._count)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < a._count; i++)
{
if (!object.Equals(a._items[i], b._items[i]))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// event
public event EventHandler Changed;
public static bool operator ==(MyList<T> a, MyList<T> b) =>
Equals(a, b);
public static bool operator !=(MyList<T> a, MyList<T> b) =>
!Equals(a, b);
}
|
用户可以使用+=, -=订阅和取消订阅EventHandler
.NET事件委托的标准签名:
1
| void EventRaised(object sender, EventArgs args);
|
委托基于多播委托,任何事件源都支持多个订阅者
Finalizers不具有参数,不具有可访问性修饰符,也不能显式调用它们
C++ template => C# 泛型,区别:
- C# 泛型的灵活性与 C++ 模板不同。 例如,虽然可以调用 C# 泛型类中的用户定义的运算符,但是无法调用算术运算符。
- C# 不允许使用非类型模板参数,如
template C<int i> {}。 - C# 不支持显式定制化;即特定类型模板的自定义实现。
- C# 不支持部分定制化:部分类型参数的自定义实现。
- C# 不允许将类型参数用作泛型类型的基类。
- C# 不允许类型参数具有默认类型。
- 在 C# 中,泛型类型参数本身不能是泛型,但是构造类型可以用作泛型。 C++ 允许使用模板参数。
- C++ 允许在模板中使用可能并非对所有类型参数有效的代码,随后针对用作类型参数的特定类型检查此代码。 C# 要求类中编写的代码可处理满足约束的任何类型。 例如,在 C++ 中可以编写一个函数,此函数对类型参数的对象使用算术运算符
+ 和 -,在实例化具有不支持这些运算符的类型的模板时,此函数将产生错误。 C# 不允许此操作;唯一允许的语言构造是可以从约束中推断出来的构造。
interface
接口包含非抽象class或struct必须实现的一组相关功能的定义,接口可以定义 static 方法,此类方法必须具有实现,接口可为成员定义默认实现,接口不能声明实例数据,如字段、自动实现的属性或类似属性的事件
interface接口之间可以采用多重继承,类和结构也可以实现多个接口,类和结构也可以隐式转换为该接口类型
无法使用new直接实例化interface,而需要创建并分配实现接口的类实例
接口可以包含实例方法、属性、事件、索引器或这四种成员类型的任意组合。
接口可以包含静态构造函数、字段、常量或运算符。
从 C# 11 开始,非字段接口成员可以是 static abstract
接口不能包含实例字段、实例构造函数或终结器
接口成员默认是公共的,可以显式指定可访问性修饰符(如 public、protected、internal、private、protected internal 或 private protected),private 成员必须有默认实现
若要实现接口成员,实现类的对应成员必须是公共、非静态,并且具有与接口成员相同的名称和签名,实现接口的类或结构必须为所有已声明的成员提供实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| interface IEquatable<T>
{
bool Equals(T obj);
}
public class Car : IEquatable<Car>
{
public string? Make { get; set; }
public string? Model { get; set; }
public string? Year { get; set; }
// Implementation of IEquatable<T> interface
public bool Equals(Car? car)
{
return (this.Make, this.Model, this.Year) ==
(car?.Make, car?.Model, car?.Year);
}
}
|
类的属性和索引器可以为接口中定义的属性或索引器定义额外的访问器。例如,接口可能会声明包含get取值函数的属性。实现此接口的类可以声明包含get和get取值函数的同一属性
接口可从一个或多个接口继承,实现派生接口的类必须实现派生接口中的所有成员,包括派生接口的基接口的所有成员
类可能通过继承基类或继承其他接口来多次包含某一接口,但只提供该接口的实现一次,当且仅当将接口作为类定义的一部分声明(class ClassName : InterfaceName)时才提供
C# 8开始,实现接口的类/结构不一定要实现具有默认实现的成员
record
记录是一个类/结构,在下列情况下,请考虑使用记录而不是类或结构:
- 你想要定义依赖值相等性的数据模型。
- 你想要定义对象不可变的类型。
值相等性表示类型匹配且所有属性和字段值都匹配,对于其他引用类型,相等性指引用相等性,无法比较类的两个对象是否相等
记录与类的区别如下所示:
记录结构与结构的不同之处是,编译器合成了方法来确定相等性和 ToString。 编译器为位置记录结构合成 Deconstruct 方法。
编译器为 record class 中的每个主构造函数参数合成一个公共仅初始化属性。 在 record struct 中,编译器合成公共读写属性。 编译器不会在不包含 record 修饰符的 class 和 struct 类型中创建主构造函数参数的属性。
使用位置参数来声明和实例化记录:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public record Person(string FirstName, string LastName);
public static void Main()
{
Person person = new("Nancy", "Davolio");
Console.WriteLine(person);
// output: Person { FirstName = Nancy, LastName = Davolio }
}
|
值相等、with 表达式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public record Person(string FirstName, string LastName)
{
public string[] PhoneNumbers { get; init; }
}
public static void Main()
{
Person person1 = new("Nancy", "Davolio") { PhoneNumbers = new string[1] };
Console.WriteLine(person1);
// output: Person { FirstName = Nancy, LastName = Davolio, PhoneNumbers = System.String[] }
Person person2 = person1 with { FirstName = "John" };
Console.WriteLine(person2);
// output: Person { FirstName = John, LastName = Davolio, PhoneNumbers = System.String[] }
Console.WriteLine(person1 == person2); // output: False
person2 = person1 with { PhoneNumbers = new string[1] };
Console.WriteLine(person2);
// output: Person { FirstName = Nancy, LastName = Davolio, PhoneNumbers = System.String[] }
Console.WriteLine(person1 == person2); // output: False
person2 = person1 with { };
Console.WriteLine(person1 == person2); // output: True
}
|
匿名类型
将一组只读属性封装到单个对象中无需事先指定类型,类型名由编译器生成,无法在源码中使用
1
2
3
4
5
| var v = new { Amount = 108, Message = "Hello" };
// Rest the mouse pointer over v.Amount and v.Message in the following
// statement to verify that their inferred types are int and string.
Console.WriteLine(v.Amount + v.Message);
|
匿名类型包含一个或多个公共只读属性,用来初始化属性的表达式不能为 null、匿名函数或指针类型
匿名类型通常用在查询表达式的 select 子句中,最常见的方案是用其他类型的属性初始化匿名类型
其他使用var的场景:
1
2
3
| for (var x = 1; x < 10; x++)
foreach (var item in list) {...}
using (var file = new StreamReader("C:\\myfile.txt")) {...}
|
匿名键入元素的数组:
1
| var anonArray = new[] { new { name = "apple", diam = 4 }, new { name = "grape", diam = 1 }};
|
匿名类型是class类型,它们直接派生自object,并且无法强制转换为除object外的任何类型
匿名类型支持采用 with 表达式形式的非破坏性修改:
1
2
| var apple = new { Item = "apples", Price = 1.35 };
var onSale = apple with { Price = 0.79 };
|
无法将字段、属性、时间或方法的返回类型/形参声明为具有匿名类型,可将参数作为类型 object 进行声明,但违背了强类型的目的
匿名类型确实会重写 ToString 方法,将用大括号括起来的每个属性的名称和 ToString 输出连接起来
元组
元组可作为返回值:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class Example
{
public static void Main()
{
var result = QueryCityData("New York City");
var city = result.Item1;
var pop = result.Item2;
var size = result.Item3;
// Do something with the data.
}
private static (string, int, double) QueryCityData(string name)
{
if (name == "New York City")
return (name, 8175133, 468.48);
return ("", 0, 0);
}
}
|
三种方式析构元组:
- 可以在括号内显式声明每个字段的类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public static void Main()
{
(string city, int population, double area) = QueryCityData("New York City");
// Do something with the data.
}
|
- 可使用
var 关键字,以便 C# 推断每个变量的类型。 将 var 关键字放在括号外。 以下示例在析构由 QueryCityData 方法返回的三元组时使用类型推理。1,2可结合
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public static void Main()
{
var (city, population, area) = QueryCityData("New York City");
(string city, var population, var area) = QueryCityData("New York City");
// Do something with the data.
}
|
- 可将元组析构到已声明的变量中,可在析构中混合使用变量声明和赋值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public static void Main()
{
string city = "Raleigh";
int population = 458880;
(city, population, double area) = QueryCityData("New York City");
// Do something with the data.
}
|
可自定义Decontrust方法析构
语句类型
- Local variable declaration.
- Local constant declaration.
- Expression statement.
if statement.switch statement.while statement.do statement.for statement.foreach statement.break statement.continue statement.goto statement.return statement.yield statement.throw statements and try statements.checked and unchecked statements.lock statement.using statement.
C#支持类似sql的查询语句
major language areas
通用集合类型列在 System.Collections.Generic 名称空间;特殊的比如System.Span<T>用于访问在栈上连续内存,System.Memory<T>用于访问堆上的连续内存
数组
隐式派生自System.Array类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| int[] a1 = new int[10];
int[,] a2 = new int[10, 5];
int[,,] a3 = new int[10, 5, 2];
int[] a4 = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 };
int[] a5 = a4;
foreach (int item in a) {
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
|
字符串插值:Console.WriteLine($"{var}")
委托和Lambda表达式
委托类型,类似函数指针,表示对具有特定参数列表和返回类型的方法的引用
1
| delegate double Function(double x);
|
委托可以引用Lambda表达式创建匿名函数、引用静态方法或实例方法
委托不知道或不在意其所引用的方法的类。 引用的方法必须具有与委托相同的参数和返回类型
委托提供后期绑定机制
异步async/await
async修饰符声明函数为异步方法,await通知编译器异步等待结果完成
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public async Task<int> RetrieveDocsHomePage()
{
var client = new HttpClient();
byte[] content = await client.GetByteArrayAsync("https://learn.microsoft.com/");
Console.WriteLine($"{nameof(RetrieveDocsHomePage)}: Finished downloading.");
return content.Length;
}
|
属性
类型、成员等实体支持使用修饰符控制行为,所有特性类都派生自 .NET 库提供的 Attribute 基类,如果特性的名称以 Attribute 结尾,那么可以在引用特性时省略这部分名称
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public class HelpAttribute : Attribute
{
string _url;
string _topic;
public HelpAttribute(string url) => _url = url;
public string Url => _url;
public string Topic
{
get => _topic;
set => _topic = value;
}
}
[Help("https://learn.microsoft.com/dotnet/csharp/tour-of-csharp/features")]
public class Widget
{
[Help("https://learn.microsoft.com/dotnet/csharp/tour-of-csharp/features", Topic = "Display")]
public void Display(string text) { }
}
|
在运行时使用反射来读取和操纵特性定义的元数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| Type widgetType = typeof(Widget);
object[] widgetClassAttributes = widgetType.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(HelpAttribute), false);
if (widgetClassAttributes.Length > 0)
{
HelpAttribute attr = (HelpAttribute)widgetClassAttributes[0];
Console.WriteLine($"Widget class help URL : {attr.Url} - Related topic : {attr.Topic}");
}
System.Reflection.MethodInfo displayMethod = widgetType.GetMethod(nameof(Widget.Display));
object[] displayMethodAttributes = displayMethod.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(HelpAttribute), false);
if (displayMethodAttributes.Length > 0)
{
HelpAttribute attr = (HelpAttribute)displayMethodAttributes[0];
Console.WriteLine($"Display method help URL : {attr.Url} - Related topic : {attr.Topic}");
}
|
程序框架
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| // A skeleton of a C# program
using System;
// Your program starts here:
Console.WriteLine("Hello world!");
namespace YourNamespace
{
class YourClass
{
}
struct YourStruct
{
}
interface IYourInterface
{
}
delegate int YourDelegate();
enum YourEnum
{
}
namespace YourNestedNamespace
{
struct YourStruct
{
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Before C# 9 Your program starts here...
Console.WriteLine("Hello world!");
}
}
}
|
Main
C# 程序中只能有一个入口点。 如果多个类包含 Main 方法,必须使用 StartupObject 编译器选项来编译程序,以指定将哪个 Main 方法用作入口点
Main 方法是可执行程序的入口点,也是程序控制开始和结束的位置。Main 在类或结构中声明。Main 必须是static,它不需要是public。封闭类或结构不一定要是静态的。Main 的返回类型可以是 void、int、Task 或 Task<int>。- 当且仅当
Main 返回 Task 或 Task<int> 时,Main 的声明可包括 async 修饰符。 这明确排除了 async void Main 方法。 - 使用或不使用包含命令行自变量的
string[] 参数声明 Main 方法都行。 可以手动添加此形参,也可以使用 GetCommandLineArgs() 方法来获取命令行实参。 参数被读取为从零开始编制索引的命令行自变量。 与C和C++不同,程序的名称不被视为 args 数组中的第一个命令行实参,但它是 GetCommandLineArgs() 方法中的第一个元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public static void Main() { }
public static int Main() { }
public static void Main(string[] args) { }
public static int Main(string[] args) { }
public static async Task Main() { }
public static async Task<int> Main() { }
public static async Task Main(string[] args) { }
public static async Task<int> Main(string[] args) { }
|
如果不使用 Main 的返回值,则返回 void 或 Task 可使代码变得略微简单。
还可使用 Environment.CommandLine 或 Environment.GetCommandLineArgs 从控制台或 Windows 窗体应用程序的任意位置访问命令行参数
命令行参数:dotnet run -- [args]
顶级语句
顶级语句隐式位于全局命名空间中。如果包含 using 指令,则它们必须首先出现在文件中;具有顶级语句的文件还可以包含命名空间和类型定义,但它们必须位于顶级语句之后。
顶级语句可以引用 args 变量来访问输入的任何命令行参数。 args 变量永远不会为 null,但如果未提供任何命令行参数,则其 Length 将为零。
退出时返回值使用return
隐式入口点方法
编译器会生成一个方法,作为具有顶级语句的项目的程序入口点。 此方法的名称实际上并不是 Main,而是代码无法直接引用的实现细节。 方法的签名取决于顶级语句是包含 await 关键字还是 return 语句。 下表显示了方法签名的外观,为了方便起见,在表中使用了方法名称 Main。
| 顶级代码包含 | 隐式 Main 签名 |
|---|
await 和 return | static async Task<int> Main(string[] args) |
await | static async Task Main(string[] args) |
return | static int Main(string[] args) |
非 await 或 return | static void Main(string[] args) |
namespace
- 通过使用
. 运算符分隔它们。 using 指令可免去为每个类指定命名空间的名称。global 命名空间是“根”命名空间:global::System 始终引用 .NET System 命名空间。
输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| string s = "The answer is " + 5.ToString();
// Outputs: "The answer is 5"
Console.WriteLine(s);
Type type = 12345.GetType();
// Outputs: "System.Int32"
Console.WriteLine(type);
|
通过在内插表达式后面添加一个逗号(“,”)并指定“最小”字段宽度来指定对齐方式。 如果指定的值是正数,则该字段为右对齐。 如果它为负数,则该字段为左对齐。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| Console.WriteLine($"Inventory on {DateTime.Now:d}");
Console.WriteLine(" ");
Console.WriteLine($"|{"Item",-25}|{"Quantity",10}|");
foreach (var item in inventory)
Console.WriteLine($"|{item.Key,-25}|{item.Value,10}|");
Console.WriteLine($"[{DateTime.Now,-20:d}] Hour [{DateTime.Now,-10:HH}] [{1063.342,15:N2}] feet");
|
OOP
封装有时称为面向对象的编程的第一支柱或原则
对象是否相等
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public struct Person
{
public string Name;
public int Age;
public Person(string name, int age)
{
Name = name;
Age = age;
}
}
Person p1 = new Person("Wallace", 75);
Person p2 = new Person("", 42);
p2.Name = "Wallace";
p2.Age = 75;
if (p2.Equals(p1))
Console.WriteLine("p2 and p1 have the same values.");
// Output: p2 and p1 have the same values.
|
派生类定义相同名称和签名声明成员来隐藏基类成员,可选使用new修饰符(不使用编译器会警告)
多态性常被视为自封装和继承之后,面向对象的编程的第三个支柱
- 在运行时,在方法参数和集合或数组等位置,派生类的对象可以作为基类的对象处理。 在出现此多形性时,该对象的声明类型不再与运行时类型相同。
- 基类可以定义并实现虚方法,派生类可以重写这些方法,即派生类提供自己的定义和实现。 在运行时,客户端代码调用该方法,CLR 查找对象的运行时类型,并调用虚方法的重写方法。 你可以在源代码中调用基类的方法,执行该方法的派生类版本。
派生类使用base访问基类成员
功能技术
模式匹配
测试表达式是否具有特定特征
null check
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| int? maybe = 12;
if (maybe is int number)
{
Console.WriteLine($"The nullable int 'maybe' has the value {number}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("The nullable int 'maybe' doesn't hold a value");
}
|
上述代码是声明模式,用于测试变量类型并将其分配给新变量
可以添加 not 模式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| string? message = "This is not the null string";
if (message is not null)
{
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
|
type test
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public static T MidPoint<T>(IEnumerable<T> sequence)
{
if (sequence is IList<T> list)
{
return list[list.Count / 2];
}
else if (sequence is null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(sequence), "Sequence can't be null.");
}
else
{
int halfLength = sequence.Count() / 2 - 1;
if (halfLength < 0) halfLength = 0;
return sequence.Skip(halfLength).First();
}
}
|
比较离散值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public State PerformOperation(Operation command) =>
command switch
{
Operation.SystemTest => RunDiagnostics(),
Operation.Start => StartSystem(),
Operation.Stop => StopSystem(),
Operation.Reset => ResetToReady(),
// _ 弃元模式
_ => throw new ArgumentException("Invalid enum value for command", nameof(command)),
};
// string 也是可以的
// string 可换成ReadOnlySpan<char>/Span<char>
public State PerformOperation(string command) =>
command switch
{
"SystemTest" => RunDiagnostics(),
"Start" => StartSystem(),
"Stop" => StopSystem(),
"Reset" => ResetToReady(),
_ => throw new ArgumentException("Invalid string value for command", nameof(command)),
};
|
关系模式
处理比较:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| string WaterState(int tempInFahrenheit) =>
tempInFahrenheit switch
{
(> 32) and (< 212) => "liquid",
< 32 => "solid",
> 212 => "gas",
32 => "solid/liquid transition",
212 => "liquid / gas transition",
};
|
多个输入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public record Order(int Items, decimal Cost);
public decimal CalculateDiscount(Order order) =>
order switch
{
{ Items: > 10, Cost: > 1000.00m } => 0.10m,
{ Items: > 5, Cost: > 500.00m } => 0.05m,
{ Cost: > 250.00m } => 0.02m,
null => throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(order), "Can't calculate discount on null order"),
var someObject => 0m,
};
|
如果 Order 类型定义了适当的 Deconstruct 方法,则可以省略模式的属性名称,并使用析构检查属性:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public decimal CalculateDiscount(Order order) =>
order switch
{
( > 10, > 1000.00m) => 0.10m,
( > 5, > 50.00m) => 0.05m,
{ Cost: > 250.00m } => 0.02m,
null => throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(order), "Can't calculate discount on null order"),
var someObject => 0m,
};
|
列表模式
检查列表或数组中的元素,提供了一种方法,将模式应用于序列的任何元素。 此外,还可以应用弃元模式 (_) 来匹配任何元素,或者应用切片模式来匹配零个或多个元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| decimal balance = 0m;
foreach (string[] transaction in ReadRecords())
{
balance += transaction switch
{
[_, "DEPOSIT", _, var amount] => decimal.Parse(amount),
[_, "WITHDRAWAL", .., var amount] => -decimal.Parse(amount),
[_, "INTEREST", var amount] => decimal.Parse(amount),
[_, "FEE", var fee] => -decimal.Parse(fee),
_ => throw new InvalidOperationException($"Record {string.Join(", ", transaction)} is not in the expected format!"),
};
Console.WriteLine($"Record: {string.Join(", ", transaction)}, New balance: {balance:C}");
}
|
弃元
_,弃元相当于未赋值的变量,它们没有值,可以使用弃元指定 Lambda 表达式中不使用的输入参数
可使用独立弃元来指示要忽略的任何变量
语言集成查询LINQ
可使用相同的基本查询表达式模式来查询和转换 SQL 数据库、ADO .NET 数据集、XML 文档和流以及 .NET 集合中的数据
应用程序始终将源数据视为 IEnumerable<T> 或 IQueryable<T> 集合
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| // Data source.
int[] scores = { 90, 71, 82, 93, 75, 82 };
// Query Expression.
IEnumerable<int> scoreQuery = //query variable
from score in scores //required
where score > 80 // optional
orderby score descending // optional
select score; //must end with select or group
// Execute the query to produce the results
foreach (int testScore in scoreQuery)
{
Console.WriteLine(testScore);
}
// Output: 93 90 82 82
|
使用 group 子句可生成按指定键组织的组的序列
1
2
3
| var queryCountryGroups =
from country in countries
group country by country.Name[0];
|
使用 select 子句可生成所有其他类型的序列,可以用于将源数据转换为新类型的序列,即投影
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| // Here var is required because the query
// produces an anonymous type.
var queryNameAndPop =
from country in countries
select new
{
Name = country.Name,
Pop = country.Population
};
|
可以在 select 或 group 子句中使用 into 关键字创建存储查询的临时标识符,若在分组或选择操作之后必须对查询执行其他查询操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| // percentileQuery is an IEnumerable<IGrouping<int, Country>>
var percentileQuery =
from country in countries
let percentile = (int)country.Population / 10_000_000
group country by percentile into countryGroup
where countryGroup.Key >= 20
orderby countryGroup.Key
select countryGroup;
|
使用 orderby 子句可按升序或降序对结果进行排序。 还可以指定次要排序顺序,默认ascending
从方法返回查询(非结果):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| // QueryMethod1 returns a query as its value.
IEnumerable<string> QueryMethod1(int[] ints) =>
from i in ints
where i > 4
select i.ToString();
// QueryMethod2 returns a query as the value of the out parameter returnQ
void QueryMethod2(int[] ints, out IEnumerable<string> returnQ) =>
returnQ =
from i in ints
where i < 4
select i.ToString();
|
若要在不执行 foreach 循环的情况下评估查询并存储其结果,只需调用查询变量上的以下方法之一:
按匿名类型分组:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| var groupByCompoundKey =
from student in students
group student by new
{
FirstLetter = student.LastName[0],
IsScoreOver85 = student.ExamScores[0] > 85
} into studentGroup
orderby studentGroup.Key.FirstLetter
select studentGroup;
|
动态指定谓词筛选器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| int[] ids = { 111, 114, 112 };
var queryNames =
from student in students
where ids.Contains(student.ID)
select new
{
student.LastName,
student.ID
};
|
异常处理
异常使用throw创建
异常具有以下属性:
- 异常是最终全都派生自
System.Exception 的类型。 - 在可能抛出异常的语句周围使用
try 代码块。 - 在
try 代码块中出现异常后,控制流会跳转到调用堆栈中任意位置上的首个相关异常处理程序。 在 C# 中,catch 关键字用于定义异常处理程序。 - 如果给定的异常没有对应的异常处理程序,那么程序会停止执行,并显示错误消息。
- 除非可以处理异常并让应用程序一直处于已知状态,否则不捕获异常。 如果捕获
System.Exception,使用 catch 代码块末尾的 throw 关键字重新抛出异常。 - 如果
catch 代码块定义异常变量,可以用它来详细了解所发生的异常类型。 - 使用
throw 关键字,程序可以显式生成异常。 - 异常对象包含错误详细信息,如调用堆栈的状态和错误的文本说明。
- 即使引发异常,
finally 代码块中的代码仍会执行。 使用 finally 代码块可释放资源。例如,关闭在 try 代码块中打开的任何流或文件。 - .NET 中的托管异常在 Win32 结构化异常处理机制的基础之上实现。 有关详细信息,请参阅结构化异常处理 (C/C++) 和速成教程:深入了解 Win32 结构化异常处理。
如果引发异常之后没有在调用堆栈上找到兼容的 catch 块,则会出现以下三种情况之一:
异常处理:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| try
{
// Code to try goes here.
}
catch (SomeSpecificException ex)
{
// Code to handle the exception goes here.
}
finally
{
// Code to execute after the try (and possibly catch) blocks
// goes here.
}
|
当基本操作失败时,.NET 运行时会自动引发一些异常。 这些异常及其错误条件在下表中列出。
Coding Style
命名规则
标识符:
- 标识符必须以字母或下划线 (
_) 开头。 - 标识符可以包含 Unicode 字母字符、十进制数字字符、Unicode 连接字符、Unicode 组合字符或 Unicode 格式字符。 有关 Unicode 类别的详细信息,请参阅 Unicode 类别数据库。
可以在标识符上使用@前缀来声明与C#关键字匹配的标识符
命名约定:.NET Runtime 团队的编码风格
- 接口名称以大写字母
I开头 - 属性类型以单词
Attribute结尾 - 枚举类型对非标记使用单数名词,对标记使用复数名词。
- 标识符不应包含两个连续的下划线 (
_) 字符。 这些名称保留给编译器生成的标识符 - 将 PascalCase 用于类名和方法名称
- 将 camelCase 用于方法参数、局部变量和专用字段
- 将 PascalCase 用于常量名,包括字段和局部常量
- 专用实例字段以下划线(
_)开头 - 静态字段以
s_开头。 请注意,这不是默认的 Visual Studio 行为,也不是框架设计准则的一部分,但在 editorconfig 中可配置 - 避免使用单字母名称,但简单循环计数器除外。 此外,描述 C# 构造的语法示例通常使用与 C# 语言规范中使用的约定相匹配的以下单字母名称。 语法示例是规则的例外
- 将
S用于结构,将C用于类。 - 将
M用于方法。 - 将
v用于变量,将p用于参数。 - 将
r用于ref参数。
在命名class、Interface、struct或delegate类型时,使用Pascal大小写
在命名字段、属性和事件等类型的public成员时,使用pascal大小写。此外,对所有方法和本地函数使用pascal大小写。
编写位置记录时,对参数使用pascal大小写,因为它们是记录的公共属性。
在命名private或internal字段时,使用驼峰式大小写(“camelCasing”),并对它们添加_作为前缀,使用为 private 或 internal 的static 字段时 请使用 s_ 前缀,对于线程静态,请使用 t_
将 using 指令放在命名空间声明之外
